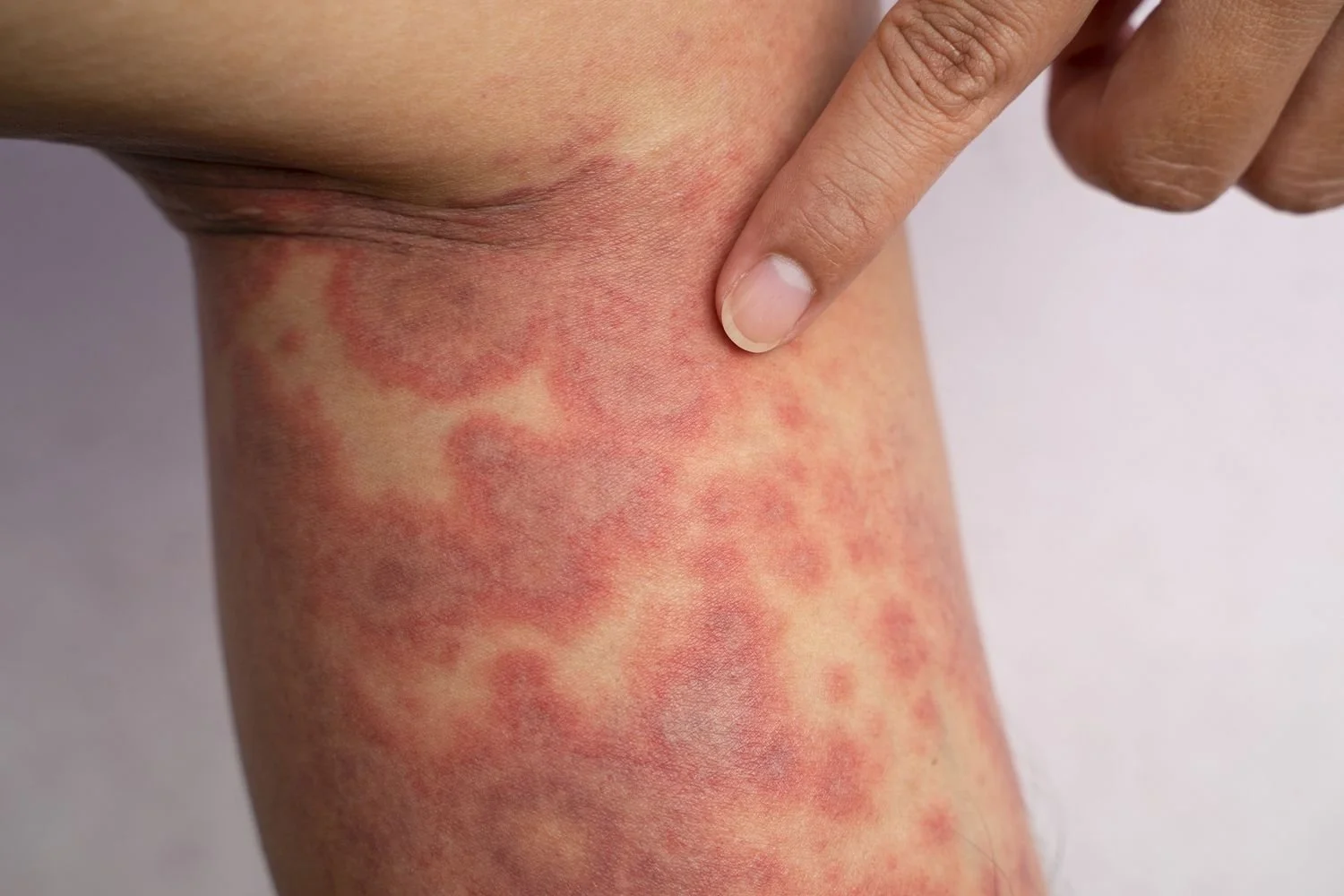
Say Goodbye to Flare-Ups: How Dermatologists Tackle Eczema for Good
Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a chronic skin condition that affects millions of people worldwide. Characterized by inflamed, itchy, and red patches, eczema can be a frustrating and sometimes painful experience. As a medical dermatologist, I often see patients struggling with this condition, and the good news is that there are effective strategies to manage and even minimize flare-ups. In this article, we'll dive deep into the causes of eczema, treatment options, and tips for preventing those annoying flare-ups. We’ll also answer some of the most frequently asked questions to help you better understand this common skin condition.
What is Eczema?
Eczema is a condition that causes patches of skin to become red, inflamed, itchy, and sometimes cracked or blistered. While eczema can appear anywhere on the body, it often affects the face, hands, and feet, as well as the insides of elbows and knees. The severity of eczema varies from person to person; for some, it can be mild and occasional, while others experience severe and frequent flare-ups.
What Causes Eczema?
The exact cause of eczema is still not fully understood, but it's believed to result from a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Individuals with a family history of eczema, asthma, or hay fever are more likely to develop the condition. The skin of eczema sufferers often has a weakened barrier, making it more susceptible to irritants, allergens, and infections.
Triggers that can cause flare-ups include:
Irritants: Soaps, detergents, fragrances, and certain fabrics.
Allergens: Pet dander, dust mites, mold, and pollen.
Weather conditions: Cold, dry weather or hot, humid climates.
Stress: Emotional stress can exacerbate symptoms.
Food allergies: In some cases, foods like dairy, eggs, or nuts can trigger eczema.
How Dermatologists Treat Eczema
Eczema can be a lifelong condition, but with the right approach, flare-ups can be minimized and the skin can be kept healthy. Dermatologists use a variety of treatments tailored to the individual’s needs. Here's how we tackle eczema for good:
1. Moisturizers and Emollients
One of the simplest but most effective treatments for eczema is regular moisturization. Eczema-prone skin is often dry and prone to cracking, so using thick moisturizers and emollients helps to restore the skin’s natural barrier. I recommend applying fragrance-free creams or ointments right after bathing to lock in moisture.
2. Topical Steroids
When flare-ups occur, they can be quite severe. Topical corticosteroids are the first line of defense to reduce inflammation and itching quickly. These creams or ointments should be applied sparingly and only as directed by your dermatologist to avoid potential side effects like thinning of the skin.
3. Topical Calcineurin Inhibitors
For patients who cannot use steroids or need an alternative, we sometimes prescribe topical calcineurin inhibitors such as tacrolimus or pimecrolimus. These medications help reduce inflammation without the side effects associated with steroids.
4. Oral Medications
For severe cases of eczema, oral medications like corticosteroids, antihistamines, or immune-modulating drugs may be necessary. These medications are usually prescribed for short-term use to bring eczema under control.
5. Phototherapy
Light therapy, or phototherapy, is an option for those who have not responded well to topical treatments. It involves exposing the skin to controlled amounts of natural sunlight or artificial ultraviolet A (UVA) and ultraviolet B (UVB) rays, which can help reduce inflammation and improve skin healing.
6. Biologics
In recent years, biologics such as dupilumab (Dupixent) have emerged as a breakthrough treatment for moderate-to-severe eczema. Biologics target specific parts of the immune system involved in eczema flare-ups and can significantly reduce symptoms over time.
7. Lifestyle Modifications
Treating eczema isn’t just about medications. Managing triggers through lifestyle changes is crucial. This includes wearing breathable, cotton fabrics, using hypoallergenic skin products, avoiding hot showers, and reducing stress through mindfulness or relaxation techniques.
Dry skin tends to be more or less constant, depending on environmental factors like humidity and skincare routine. Psoriasis, on the other hand, often follows a cyclical pattern, with periods of remission followed by flare-ups. These flare-ups can be triggered by various factors, including stress, infections, skin injuries, and certain medications.
During a flare-up, the symptoms of psoriasis can become more severe, with an increase in the size and number of plaques, more intense itching, and greater discomfort. Recognizing this pattern can help distinguish psoriasis from chronic dry skin.
What to Do If You Suspect Psoriasis
If you recognize any of these signs, it's essential to consult a medical dermatologist for an accurate diagnosis. Psoriasis is a chronic condition that requires a tailored treatment plan, which may include topical treatments, phototherapy, or systemic medications. Early intervention can help manage symptoms and reduce the risk of complications such as psoriatic arthritis
5 Frequently Asked Questions About Eczema
FAQ Eczema:
1. Can Eczema Be Cured?
Unfortunately, there is no permanent cure for eczema. However, many people experience long periods of remission with the right treatment. Our goal as dermatologists is to manage symptoms effectively and minimize flare-ups, allowing patients to live more comfortably.
2. Is Eczema Contagious?
No, eczema is not contagious. You cannot catch eczema by coming into contact with someone who has the condition. It is a non-infectious skin disease, often linked to genetic and environmental factors.
3. How Can I Prevent Eczema Flare-Ups?
Preventing flare-ups is all about identifying and avoiding triggers. Common steps include using fragrance-free and hypoallergenic skincare products, wearing soft and non-irritating fabrics, staying hydrated, and keeping stress levels in check. Regular moisturizing is key to maintaining healthy skin and preventing dryness.
4. Can Food Allergies Cause Eczema?
While food allergies don't directly cause eczema, they can trigger flare-ups in some individuals. Common culprits include dairy, eggs, soy, and nuts. If you suspect that food is triggering your eczema, consult with a dermatologist or an allergist for testing and management strategies.
5. When Should I See a Dermatologist for Eczema?
If over-the-counter treatments and home remedies aren’t providing relief, it’s time to see a dermatologist. You should also seek professional help if you experience severe itching, skin infections, or if eczema is significantly affecting your quality of life.
Tips for Managing Eczema Long-Term
Dealing with eczema requires a proactive approach, and here are a few tips that can help:
Establish a skincare routine: Consistency is key when managing eczema. Stick to a daily regimen of moisturizing and gentle cleansing.
Identify and avoid triggers: Whether it’s certain soaps, fabrics, or even foods, knowing your triggers will help you minimize flare-ups.
Stay hydrated: Hydration is not just about water intake; it’s also about maintaining moisture on your skin. Use a humidifier during dry weather to keep your skin hydrated.
Use prescription treatments as needed: Don’t hesitate to use prescribed treatments like topical steroids or calcineurin inhibitors when flare-ups occur, but always follow your dermatologist’s advice.
Manage stress: Stress can exacerbate eczema, so incorporating relaxation techniques like yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises can be beneficial.
Conclusion
Eczema may be a chronic condition, but that doesn't mean it has to control your life. With the right treatment plan, including moisturizers, medications, and lifestyle modifications, you can manage eczema symptoms and enjoy long-lasting relief. By working closely with a dermatologist, you can tailor your approach to what works best for your skin and say goodbye to those flare-ups for good.
If you’re struggling with eczema and need expert advice, schedule an appointment with a board-certified dermatologist today. Together, we can find a personalized treatment plan to help you live more comfortably.